Science


Nuclear Engineering: http://engineering.purdue.edu/NE
Facebook: http://bit.ly/PurdueNE-Facebook
Twitter: https://twitter.com/PurdueNuclear
Instagram: https://instagram.com/purduenuclear @purduenuclear
#purdue #nuclearengineering #nuclearenergy


For accessing 7Activestudio videos on mobile Download SCIENCETUTS App to Access 120+ hours of Free digital content.
For more information:
http://www.7activestudio.com
info@7activestudio.com
http://www.7activemedical.com/
info@7activemedical.com
http://www.sciencetuts.com/
Contact: +91- 9700061777,
040-64501777 / 65864777
7 Active Technology Solutions Pvt.Ltd. is an educational 3D digital content provider for K-12. We also customise the content as per your requirement for companies platform providers colleges etc . 7 Active driving force "The Joy of Happy Learning" -- is what makes difference from other digital content providers. We consider Student needs, Lecturer needs and College needs in designing the 3D & 2D Animated Video Lectures. We are carrying a huge 3D Digital Library ready to use.
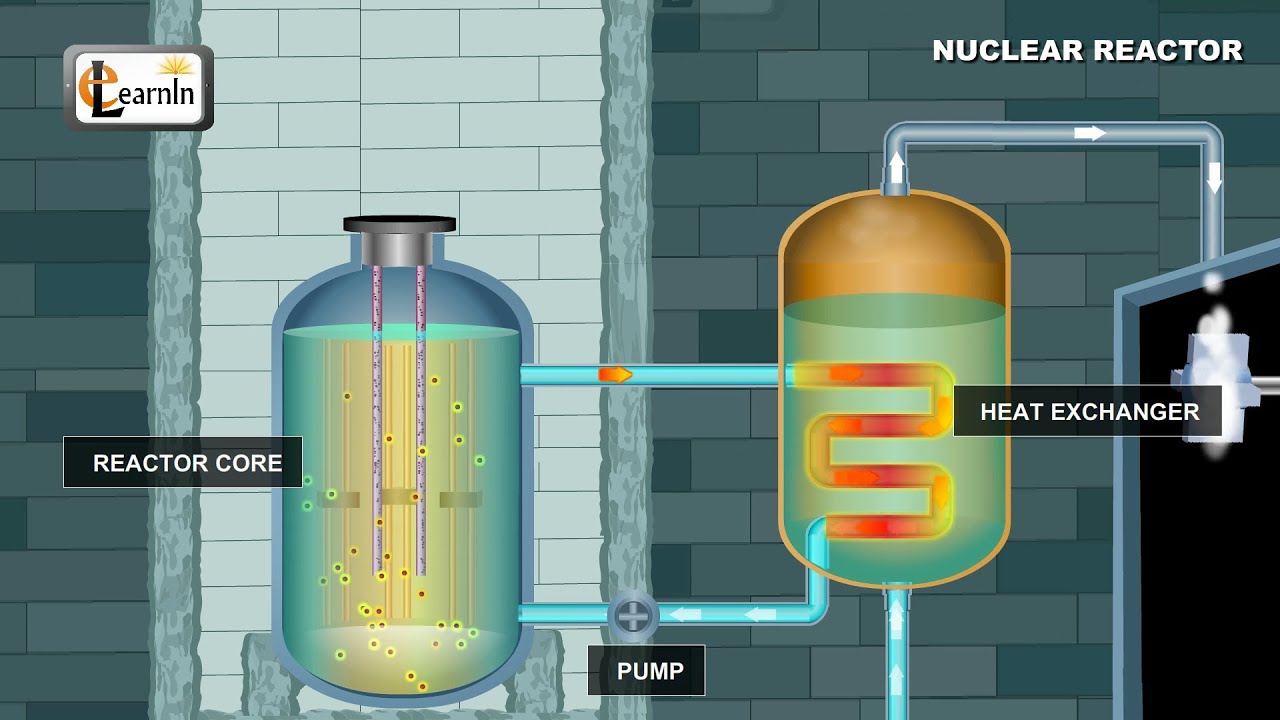
Nuclear power plants obtain the heat needed to produce steam through a physical process. This process, called fission, entails the splitting of atoms of uranium in a nuclear reactor. The uranium fuel consists of small, hard ceramic pellets that are packaged into long, vertical tubes.


Some people think radiation is a scary word but really is just the movement of particles or waves through space, learn all about nuclear radiation in this GCSE / K12 video.
Get in touch: vsteam@fusion-universal.com
Find out more: http://www.thevirtualschool.com
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/virtualschooluk
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/virtualschooluk
Teach the world.
This video is distributed under a Creative Commons License:
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs
CC BY-NC-ND


Download SCIENCETUTS App to Access 120+ hours of Free content.
For more information:
http://www.7activestudio.com
info@7activestudio.com
http://www.7activemedical.com/
info@7activemedical.com
http://www.sciencetuts.com/
Contact: +91- 9700061777,
040-64501777 / 65864777
7 Active Technology Solutions Pvt.Ltd. is an educational 3D digital content provider for K-12. We also customise the content as per your requirement for companies platform providers colleges etc . 7 Active driving force "The Joy of Happy Learning" -- is what makes difference from other digital content providers. We consider Student needs, Lecturer needs and College needs in designing the 3D & 2D Animated Video Lectures. We are carrying a huge 3D Digital Library ready to use.
A boiling water reactor uses 235U, enriched as uranium dioxide, as its fuel. The fuel is assembled into rods housed in a steel vessel that is submerged in water. The nuclear fission causes the water to boil, generating steam.
In a nuclear power reactor, the energy released is used as heat to make steam to generate electricity. (In a research reactor the main purpose is to utilise the actual neutrons produced in the core. In most naval reactors, steam drives a turbine directly for propulsion.)


A lot of people talk about it, but what is it anyway?
----------
Simpsons Footage from Season 4, Episode 12 "Marge Vs. The Monorail" from Fox
Family Guy Footage from Season 13, Episode 1 "The Simpsons Guy" from Fox
Other footage:
Jet fuel burning (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VzupfyrWiew)
Magnox nuclear train crash test (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KL-xHrCIvMA)
Missile strike test (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jBp1FNceTTA)
Radioactive waste disposal (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3QXSkXHDZgU)
Black Rainbow by Pitx (http://dig.ccmixter.org/files/Pitx/19513)
----------
Find us online!
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions


"What does the future of nuclear science look like?" Find out from Sarah Don, a graduate student in Nuclear Science and Engineering and a senior operator at the MIT Nuclear Reactor. (http://web.mit.edu/nrl/www/)
----------
Find us online!
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions
Produced by: Elizabeth Choe
Editing and Animations by: Ceri Riley


It's not exactly what you see in the movies... (it's actually much cooler.)
----------
Movie clips from:
Godzilla (2014), Warner Brothers
Hulk (2003), Universal Pictures
Dr. No (1962), United Artists
Fukushima footage from Sky News
----------
Find us online!
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions


Will, Sam, and Sam (aka the Yellow Cake Boys), graduate students in nuclear engineering and management at MIT, talk about the basics and misconceptions of nuclear energy.
Learn more about our outreach events at http://k12videos.mit.edu/outreach-events
and about the Cambridge Science Festival at http://www.cambridgesciencefestival.org/Home.aspx
License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA, MIT
More information at http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-conditions


Did you know that a nuclear reactor isn't the same thing as a nuclear power plant? What a nuclear reactor can do might surprise you.
----------
Other reactor footage from:
Czech Technical University in Prague (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-VOpdolSRqg)
Los Alamos National Lab (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w4QhJEX6DiQ)
Reactor fuel image from Neutron Radiography of Irradiated Nuclear Fuel at Idaho National Laboratory (https://www.sciencedirect.com/....science/article/pii/
Elevator Music Two Point Oh by JackBillPlatypus (https://soundcloud.com/jackbil....lplatypus/elevator-m
----------
Find us online!
MIT Nuclear Reactor: https://nrl.mit.edu/
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions

Ever wonder what actually goes on, day-to-day, at a nuclear reactor? Get an insider's tour of MIT's!
----------
Find us online!
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
Leaves by airtone (http://ccmixter.org/files/airtone/34427)
Elevator Music Two Point Oh by JackBillPlatypus (https://soundcloud.com/jackbil....lplatypus/elevator-m
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions

What's the difference between a nuclear reactor and a nuclear weapon? A lot more than you'd think.
----------
Movie clips from:
Bad Boys (1995), Columbia Pictures
Chain Reaction (1996), 20th Century Fox
Nuclear test film: https://archive.org/details/gov.doe.0800013, https://archive.org/details/gov.doe.0800003, https://archive.org/details/gov.doe.0800000, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xwpgmEvlRpM
Aircraft crash test from Sandia National Laboratories (1988)
----------
Find us online!
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/MITK12
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/MITK12Videos
http://k12videos.mit.edu
----------
made with love at MIT
Creative Commons: CC BY-NC-SA, MIT
http://k12videos.mit.edu/terms-and-conditions


This Hubblecast Light highlights the exciting discovery of the first water detected on a potentially habitable planet. With data from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, water vapour has been detected in the atmosphere of a super-Earth with habitable temperatures by University College Longon (UCL) researchers.
More information and download options: http://www.spacetelescope.org/videos/heic1916a/
Subscribe to Hubblecast in iTunes! https://itunes.apple.com/gb/po....dcast/hubblecast-hd/
Receive future episodes on YouTube by pressing the Subscribe button above or follow us on Vimeo: https://vimeo.com/hubbleesa
Watch more Hubblecavideo.web_category.allst episodes: http://www.spacetelescope.org/....videos/archive/categ
Credit:
Directed by: Bethany Downer
Editing: Nico Bartmann.
Web and technical support: Mathias André and Raquel Yumi Shida.
Written by: Bethany Downer & UCL
Music: tonelabs – Orion Fog (http://tonelabs.com)
Footage and photos: ESA/Hubble, M. Kornmesser, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab


The near-term acceleration of the rate of temperature change shows an urgent need for research on the impacts of these changes for the environment and the human-built world. So, do we really need to grow into space? How can we do it in a sustainable way? It is high time for an integrated discussion of space matter with planetary concerns.
Our new comic series 'Space Rocks' will address these concerns adapted from the latest research articles. Stay tuned for more information.
Follow Infinity Eight Productions online at :
www.infinityeightproductions.com
www.linkedin.com/company/infinityeightproductions/
Search Infinity Eight Productions on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.


Announcement of winning proposals advancing to the final round of the Innovation Challenge competition.
Connect with professional judges and win prizes by spotlighting your talent and creativity in a K12 Competition. School-aged students across the U.S. who meet eligibility guidelines can participate, whether they attend a K12-powered school or not.
Our fully accredited online schools provide an outstanding balance of structure and flexibility because we record live classes. So students can complete their weekly responsibilities at their own pace, getting ahead where they can and taking extra time when needed. Explore a day in the life of real families to see how online school might work for you at
https://www.k12.com/parent-stu....dent-resources/how-o
Find an Online School in Your State
https://www.k12.com/schoolfinder.html
#k12 #k12online #onlineschool #schoolcomptition
______
Connect with K12!
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/StrideK12
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/k12learn/
Tik Tok: https://www.tiktok.com/@stridek12
Pinterest: http://pinterest.com/k12inc/


What is the importance of the accurate design of a satellite orbit?
For more information about our courses, certificates, and to watch free samples of the lectures, please visit our K12 Space Science & Satellites Academy at: http://k12-space-academy.com/ for junior students (aged 10 to 17) or visit our Remote Sensing Portal at: https://remote-sensing-portal.com/ for undergraduates, postgraduates and professionals. Also, to get notified with our offers, you can like us on our Facebook page https://www.facebook.com/BRSLabs/ and subscribe to our YouTube channel.


What Are the Perturbations that influence a Satellite's Lifetime? They are Atmospheric Drag, Earth Magnetic Field, Earth Gravity Gradient, and Solar Radiation Pressure.
For more information about our courses, certificates, and to watch free samples of the lectures, please visit our K12 Space Science & Satellites Academy at: http://k12-space-academy.com/ for junior students (aged 10 to 17) or visit our Remote Sensing Portal at: https://remote-sensing-portal.com/ for undergraduates, postgraduates and professionals. Also, to get notified with our offers, you can like us on our Facebook page https://www.facebook.com/BRSLabs/ and subscribe to our YouTube channel.