Math
Sub Category
This video contains practice problems that act as a virtual math worksheet to help master the concept of equivalent fractions.
In this video we cover:
A quick review of why equivalent fractions are important
4 examples on solving for x to find equivalent fractions
2 examples for evaluating if the fractions are equivalent
Answers for solving for equivalent fractions involve multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same number as well as finding the answer by using cross multiplication
Other Relevant Videos:
Equivalent Fractions: https://youtu.be/Y_xJugQN3AM
Cross Multiplication: https://youtu.be/tto3yHdawdY
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free printable worksheets and answer sheets, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
#equivalentfractions
#fractions
#mathtips
#mathhelp
#equivalentfractionsexamples
#mathhelpvideos
#mathbasics
#rounding #math #homeschool #mathhelp
This video shows you how to round decimals to the nearest whole number. The video focuses on looking at the one's place value and evaluating the decimal place to the right of the one's place. If it is 5 or higher, the number rounds up. If it is 4 or less, the whole number remains unchanged (rounds down).
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/SI-w1rL1ZDQ
🔴 Check out this playlist:
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
Hi! Welcome to Improved Math!
If you want to learn how to add integers using a number line, then this video is for you. In this video I walk through 4 additional examples on how to add integers using a number line. I go over adding positive and negative integers together and how to quickly know in your head what the answer should be before using the number line. Don’t forget to check out the bonus problem and leave me your answer in the comments!
Be sure to check out my introductory video on how to add integers using a number line here: https://youtu.be/B45sS50C2TU
Understanding basic math isn’t just about crunching numbers; it's about fine tuning problem-solving abilities, making informed decisions, and gaining deeper insight into the world around us. From everyday tasks to complex situations, math plays a pivotal role.
Just as important is cultivating critical thinking skills. Learning how to analyze and evaluate information is needed to arrive at well-informed conclusions. Discover why these skills are the cornerstone of innovation, creativity and rational decision-making.
Math isn’t just confined to the classroom but is essential in all aspects of life from personal finance and career success to daily decision-making and creative endeavors.
Thank you so much for watching!
💡 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
💡Share this video with a friend:
✅ Let's connect:
For email inquiries: improvedmath@gmail.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
#math #integers #homeschoolmath #mathtips
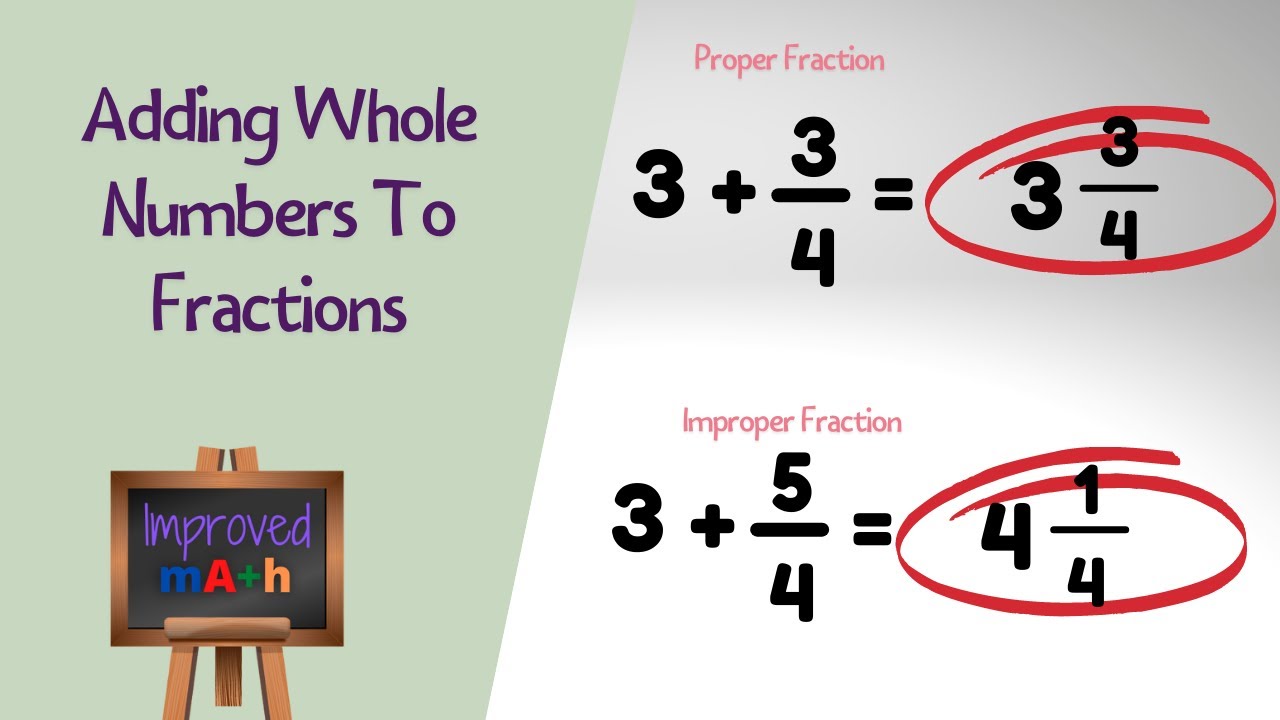
This video walks you through the step by step process for adding fractions and whole numbers.
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend:
🔴 Check out this playlist:
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
#fractions #homeschoolmath #math #homeschool #dividingfractions
This video walks you through 4 examples of dividing fractions. The key to dividing fractions is to remember the acronym KFC, which means keep, flip and change.
You want to keep your first fraction the same, flip the second fraction to its reciprocal, and change the sign to multiply. The division problem now becomes a multiplication problem and you can multiply straight across.
Try the bonus question and leave your answer in the comments!
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend:
🔴 Check out this playlist:
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
#rounding #homeschool #placevalue #mathhelp #mathvideos
Thanks for watching my video on rounding numbers to the nearest tenth. In this video, I will walk you through 4 examples for rounding to the nearest tenth. We first identify what digit is in the tenth place, then we look at the number to the right (hundredths place). If it is 5 or greater we round the tenth digit up. If it is 4 or lower we round down (which means it stays the same).
See if you can get the extra problem at the end. Leave your answer in the comments!
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/2ZumxsDleQ8
🔴 Check out this playlist:
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
This video is an introduction to the basic concepts of exponents.
In this video we cover:
What are exponents?
How to write exponents
Exponents as repeated multiplication
Examples of solving exponents
Exponential form
The standard form of exponents
The expanded form of exponents
For a free printable worksheet on exponents, check out my site here:
https://improvedmath.com/an-in....troduction-to-expone
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m not a math teacher, I’m an accountant. I know firsthand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free additional resources, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
#exponents
#standardform
#expandedform
#exponentialindex
#exponentshelp
#exponentsvideo
#helpwithexponents
#howtosolveexponents
#exponentexamples
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
#rounding #mathtips #mathhelp #homeschool #homeschooling
This video walks you through 4 examples for rounding numbers to the nearest hundred.
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/NP8hhRtpkA4
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
This video walks through the step-by-step process of converting numbers to scientific notation.
In this video we cover:
What is scientific notation
What is standard form
How to convert numbers from standard form to scientific notation
Multiplying by a power of ten
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free printable worksheets and answer sheets, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
#scientificnotation
#standardform
#exponents
#math
#mathhelpvideos
#homeshoolmath
#virtualmath
#math #homeschoolmath #integers #mathtips
Hi! Welcome to Improved Math!
If you want to learn how to add integers using a number line, then this video is for you. In this video I walk through 4 additional examples on how to add integers. In my previous video, we talked about the rules for adding integers. When adding all positive integers, your answer will always be positive. When adding all negative integers, the answer will always be negative. When adding both positive and negative integers together, you will subtract the absolute values of the integers and the answer will be in the sign of the integer with the highest absolute value. Don’t forget to check out the bonus problem and leave me your answer in the comments!
Understanding basic math isn’t just about crunching numbers; it's about fine tuning problem-solving abilities, making informed decisions, and gaining deeper insight into the world around us. From everyday tasks to complex situations, math plays a pivotal role.
Just as important is cultivating critical thinking skills. Learning how to analyze and evaluate information is needed to arrive at well-informed conclusions. Discover why these skills are the cornerstone of innovation, creativity and rational decision-making.
Math isn’t just confined to the classroom but is essential in all aspects of life from personal finance and career success to daily decision-making and creative endeavors.
Thank you so much for watching!
💡 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
💡Share this video with a friend:
✅ Let's connect:
For email inquiries: improvedmath@gmail.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
#math #homeschool #mathtips #factors #lcm
This video shows you how to use prime factorization to find the lowest common multiple. First, find your prime factors. Then create a table that lists out the factors of each number. Multiply across and that is your lowest common multiple.
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/JALEpGpi0Pg
🔴 Check out this playlist:
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
This video goes over everything you need to know to add mixed numbers.
In this video we cover:
What are mixed numbers?
Adding mixed numbers with the same denominators
Adding mixed numbers with different denominators
Adding mixed numbers vertically
Other Videos Mentioned:
Equivalent Fractions: https://youtu.be/Y_xJugQN3AM
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m not a math teacher, I’m an accountant. I know firsthand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free additional resources, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
#mixednumbers
#addingmixednumbers
#equivalentfractions
#fractions
#mathhelp
#mathtips
#mathtricks
#learnmath
#math
#freemathvideos
#homeschoolmath
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
#math #homeschoolmath #integers #mathtips
Hi! Welcome to Improved Math!
If you want to learn how to add integers using a number line, then this video is for you. In this video I walk through 4 additional examples on how to add integers. In my previous video, we talked about the rules for adding integers. When adding all positive integers, your answer will always be positive. When adding all negative integers, the answer will always be negative. When adding both positive and negative integers together, you will subtract the absolute values of the integers and the answer will be in the sign of the integer with the highest absolute value. Don’t forget to check out the bonus problem and leave me your answer in the comments!
Understanding basic math isn’t just about crunching numbers; it's about fine tuning problem-solving abilities, making informed decisions, and gaining deeper insight into the world around us. From everyday tasks to complex situations, math plays a pivotal role.
Just as important is cultivating critical thinking skills. Learning how to analyze and evaluate information is needed to arrive at well-informed conclusions. Discover why these skills are the cornerstone of innovation, creativity and rational decision-making.
Math isn’t just confined to the classroom but is essential in all aspects of life from personal finance and career success to daily decision-making and creative endeavors.
Thank you so much for watching!
💡 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
💡Share this video with a friend:
✅ Let's connect:
For email inquiries: improvedmath@gmail.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
This video shows the step-by-step process for converting scientific notation to standard form. Scientific notation creates a standard form to write numbers when they are really large or really small.
🔴 Subscribe for more free math tips and math tutorials: https://www.youtube.com/c/Impr....ovedMath?sub_confirm
In this video we cover:
Why scientific notation is used
How to convert numbers from scientific notation to standard form
The powers of ten
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free printable worksheets and answer sheets, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
#scientificnotation
#standardform
#exponents
#mathtips
#mathhelp
#homeschoolmath
#teachyourselfmath
#selfstudymath
#mathhelpvideos
Looking for an introductory tutorial on evaluating exponents? You have come to the right place!
In this video we cover:
A quick review of what exponents are and how they represent repeated multiplication. I also review briefly the powers of ten rules and how to quickly solve them. The video focuses on how to solve basic math equations when exponents are involved.
Other Videos Mentioned:
Powers of Ten: https://youtu.be/9bx4ChX82_8
Multiplying Whole Numbers By A Power of Ten: https://youtu.be/kiEMc0CrNQY
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I am passionate about math and I know firsthand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free printable worksheets and answer sheets, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
#exponents
#exponentialequations
#mathhelp
#introductiontoexponents
#basicexponents
#mathvideos
#teachyourselfmath
#selfstudymath
#homeschoolmath
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!
If you want some extra practice on comparing mixed numbers to improper fractions, you have come to the right place. This video is a virtual math worksheet for comparing fractions and includes 4 problems where you can work through them yourself, and then check your answers against mine.
In this video we cover:
How to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions
How to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers
How to use cross multiplication to compare mixed numbers and improper fractions
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/Ijv-sJgaKRw
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment and during the pandemic. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
#mathworksheetonline
#mathpracticeproblems
#fractions
#comparingfractions
#mathhelpvideos
#homeschoolmath
#selfstudymath
This video gives you 4 practice problems for adding mixed numbers that you can work on your own, and then compare your answers against mine.
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/z8-iScMK_A0
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment and during the pandemic. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
#addingmixednumbers
#fractionhelp
#mathhelpvideos
#homeschoolmath
#selfstudymath
#teachyourselfmath
#mixedfractions
If you want to know how to add positive and negative integers together, you have come to the right place. When adding both positive and negative integers, you will need to subtract (not add) the absolute value of those integers. Whichever integer has the largest absolute value is the sign the answer will be. Don’t forget to check out the bonus problem and leave me your answer in the comments!
Understanding basic math isn’t just about crunching numbers; it's about fine tuning problem-solving abilities, making informed decisions, and gaining deeper insight into the world around us. From everyday tasks to complex situations, math plays a pivotal role.
Just as important is cultivating critical thinking skills. Learning how to analyze and evaluate information is needed to arrive at well-informed conclusions. Discover why these skills are the cornerstone of innovation, creativity and rational decision-making.
Math isn’t just confined to the classroom but is essential in all aspects of life from personal finance and career success to daily decision-making and creative endeavors.
Thank you so much for watching!
💡 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
💡Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/shLLhKS8AHA
✅ Let's connect:
For email inquiries: improvedmath@gmail.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
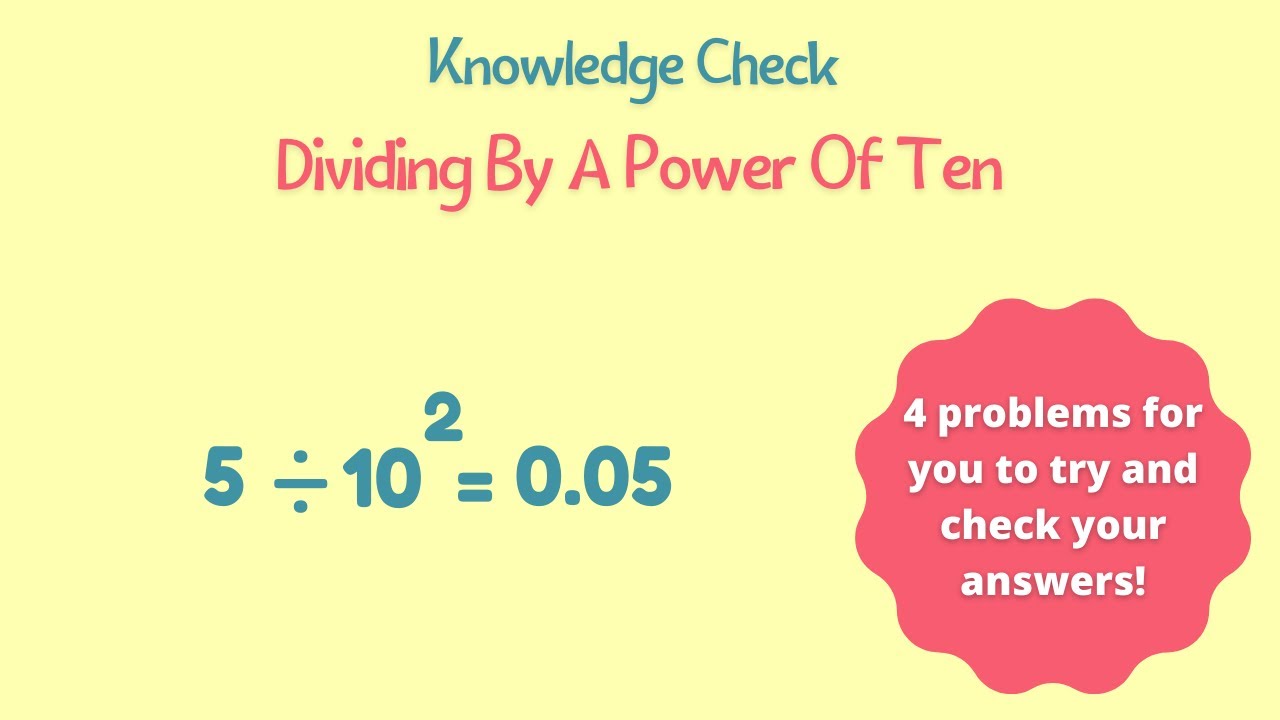
This video gives you 4 practice problems to see if you have a good understanding of the steps involved in dividing by a power of ten. There are 2 examples where you divide by a power of ten in exponential form and 2 examples where you divide by a power of ten in standard form. You can try all 4 problems on your own and then check your answers at the end.
🔴 Subscribe for more free YouTube tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
🔴 Share this video with a friend: https://youtu.be/CcAUGkHTGUI
✅ For business inquiries contact me at improvedmath@gmail.com
✅ Let's connect:
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills. These math videos are designed to help teach yourself math or provide self-study math tools to assist when additional instruction is needed. Teaching math and learning math has changed the way many students learn in this virtual environment and during the pandemic. Having on-demand math videos can provide math tutoring needed when children are not able to get help from their teachers after school hours or when trying to do math at home.
The library of math tutorials that I create can also be used as supplemental instructional material for homeschool math. Each full-length video comes with a subsequent knowledge check or math practice problems which serve as a virtual math topic worksheet to test your understanding of each skill. These videos can be paused to work out the problems on your own, then unpaused to check your answers. All of these videos can be found under the Knowledge Check playlist.
I also have a library of shorter videos (less than 1 minute in length - shorts) that are quick math tips and tricks on basic math topics. Some of these short math help videos include problems that you can work on yourself and submit your answers in the comments. They are all listed under my Math Tips and Tricks playlist.
Improved math is creating more videos every day to cover topics from 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, and 7th-grade math. The videos focus on fractions, basic math operations, geometry, and ratios but more topics are being added all the time. If there is a specific topic you would like to see covered, drop me a comment in one of my videos and let me know!
Free math help videos will be posted every Thursday and Friday. For additional math resources, check out my math help website at improvedmath.com where I post math worksheets and answers along with additional context on math basics.
Thanks for watching my channel.
In this video, I show you 4 practice problems to ensure you have mastered the concept of comparing fractions with different denominators.
In this video we cover:
Quick review of comparing fractions with different denominators
Quick review of cross multiplication
4 practice problems that you can solve at your own pace and unpause to check against the answers
Improved math is a channel created to provide additional instruction on essential math concepts. I’m passionate about math and I know first-hand how important math concepts are in the real world.
Teachers, parents, guardians, homeschoolers, and students can use these videos to help reinforce math skills.
For more information on math topics or for free printable worksheets and answer sheets, you can also visit my website at improvedmath.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/ImprovedMath
https://improvedmath.com
https://www.tiktok.com/@improvedmath1?
https://www.pinterest.com/improvedmath/
Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe!